Steps to a better environment
The key steps to a better environment and the optimal use of resources are Prevent, Reuse, Recycle, Recover and Reduced Disposal of waste. This way of thinking has been at the core of MBP’s activities ever since the business started and is now widely referred to as the circular economy.
MBP optimises by-products to reduce waste
MBP works with by-products and waste in order to move them up in this waste hierarchy. MBP’s many different experts will work with manufacturers’ technical people in order to understand how the by-products arise and to develop a suitable by-product strategy: a strategy that will optimize the potential of the individual waste and by-product streams in both the short and the long term.
At MBP, we focus only on biologically-based production and we have detailed knowledge of many different industries, applications, geographies, and legislation requirements.
Environmentally friendly by-product applications
Examples of our applications that are more environmentally friendly than disposal (such as landfilling and burning without heat recovery) include: use for animal feed (animal feeds); use as raw material in other industries (technical products); use for energy recovery (bioliquids); anaerobic digestion feedstock (biogas); and composting or nutrients for agricultural land (soil improvement).
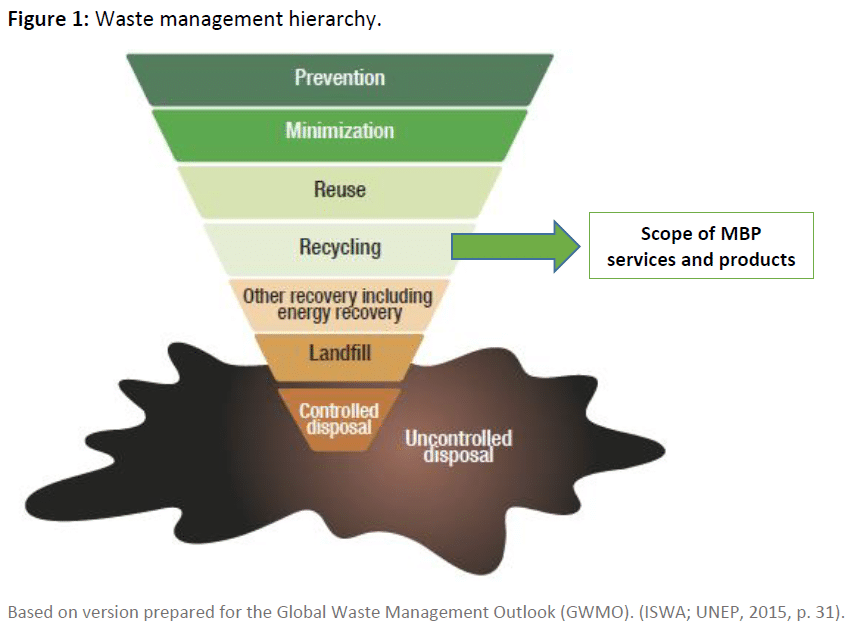
Waste management hierarchy explained
To understand the importance of recycling, we must look at the waste management hierarchy. The waste management hierarchy sets out the preferred order of handling practices, from most to least preferred, to achieve optimal environmental outcomes – from prevention to uncontrolled disposal. The premise behind this hierarchy is to show the progression of waste management and how it should be controlled.
At the bottom, we have uncontrolled disposal – this is the worst management option. For example, a company may dump their waste material in standard bins and risk contaminating other rubbish. As we progress up the hierarchy, the methods of waste management become controlled, such as recycling and reuse. The ultimate aim is to minimize waste and to prevent its occurrence entirely.
The diagram below illustrates the waste management hierarchy. Our services help improve the recycling and recovery of waste materials to benefit both the businesses we work with and the environment.
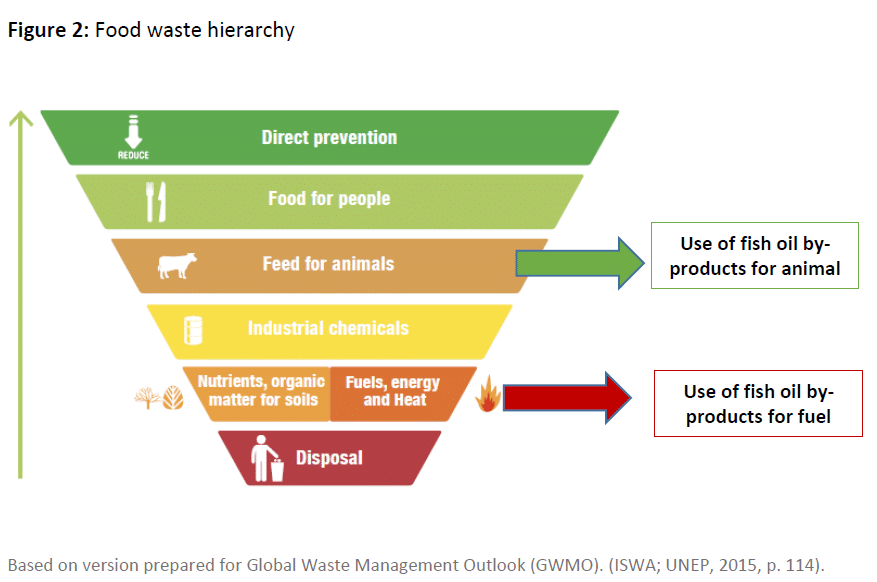
Food waste hierarchy explained
Aside from general waste management, there is also a food waste hierarchy that performs a similar function. This is a 6-step pyramid detailing the processes involved in food waste – from the disposal, to direct prevention. The aim of this diagram is to illustrate how food waste can be minimized and ultimately prevented.
The bottom step is food disposal. This could be anything from households throwing away uneaten food, through to food manufacturers disposing of waste products. Steps to prevent this include utilization as fuels and heat, production in industrial chemicals, and recycling food waste as animal feed.
Our recycling and recovery services help prevent food waste during production processes. For example, we facilitate fish oil by-products for use as both fuel and the production of animal feed. The diagram below illustrates the food waste hierarchy:
The benefits of recycling and recovery
Waste recycling is vital to the preservation of our environment. Furthermore, it contributes to business efficiency and creating circular economies. Recycling and recovery offer the following benefits:
Environmental
Improved utilization of raw materials
Less waste disposal in landfills and via burning
Creation of circular economies for industry-wide benefits
Business
Improved revenue from the sale of recycled products
Improved efficiency from 100% usage of raw materials
Streamlined business processes and production
On a global scale, everyone benefits from recycling and an efficient waste management approach. This is why our recycling and recovery services are vital for your business’s continual improvement.
Would you like to know more?

The circular economy
The circular economy is characterized by Production, Recycle and Recovery where the whole system is designed in order to minimize waste and keep the materials in use for as long as possible.

Sustainability
Protecting the environment has been part of the ideological back bone of MBP Solutions since the company was founded in 1999.